General Data Protection Regulation
GDPR? What is it?
The General Data Protection Regulation (EU) 2016/679) is a regulation by which the European Parliament, the Council of the European Union and the European Commission intend to strengthen and unify data protection for all individuals within the European Union (EU).
It is a new set of rules designed to give EU citizens more control over their personal data. It aims to simplify the regulatory environment so both citizens and businesses in the European Union can fully benefit from the digital economy.
The reforms are designed to reflect the world we live in and bring laws and obligations – including those around personal data, privacy and consent – across Europe up to speed for the internet-connected age. Fundamentally, almost every aspect of our lives revolves around data. From social media companies, to banks, retailers, and governments – almost every service we use involves the collection and analysis of our personal data.
GDPR applies to whom?
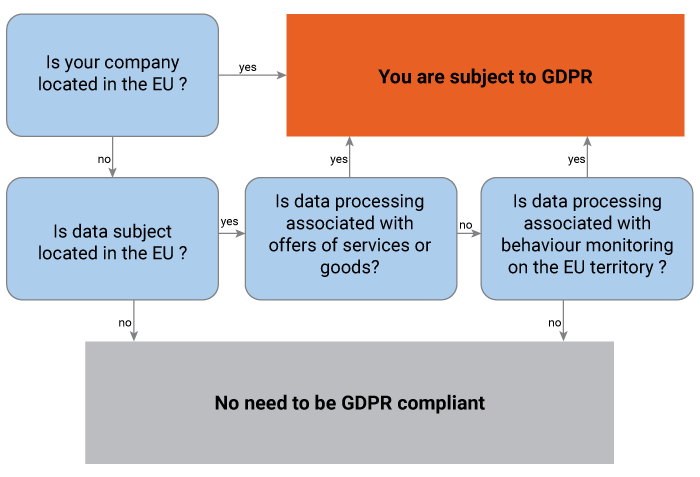
The GDPR not only applies to organizations located within the EU but also applies to organizations located outside of the EU if they offer goods or services to, or monitor the behaviour of, EU data subjects. It applies to all companies processing and holding personal data of data subjects residing in the European Union, regardless of the company’s location.
Also, the GDPR applies to ‘personal data’, which means any information relating to an identifiable person who can be directly or indirectly identified by reference to an identifier.
Does GDPR apply to Your Organization?
Penalties for non-compliance?
Organizations can be fined up to 4% of annual global turnover for breaching GDPR or €20 Million. This is the maximum fine that can be imposed for the most serious infringements e.g. not having enough customer consent to process data or violating the core of Privacy by Design concepts. There is a tiered approach to fines e.g. a company can be fined 2% for not having their records in order (article 28), not notifying the supervising authority and data subject about a breach, or not conducting impact assessment.
How can I prepare for compliance?
We are here to help you, Please fill in the contact form or speak to our consultant and our expert team will be happy to connect to help your organization comply with the new data privacy law allowing you to concentrate on your core business process and leave the worries of compliance to us.
GDPR Principles
- Principle 1: Lawfulness, Fairness and Transparency. Personal data shall be processed lawfully, fairly and in a transparent manner in relation to the data subject. This means that organizations must tell the data subject what processing will occur (transparency), the processing that must match the description given to the data subject (fairness), and one of the purposes specified in the applicable data protection regulation (lawfulness).
- Principle 2: Purpose Limitation. Personal data shall be collected for specified, explicit and legitimate purposes and not further processed in a manner that is incompatible with those purposes. This means organizations must specify exactly what the personal data collected will be used for and limit the processing of that personal data to only what is necessary to meet the specified purpose.
- Principle 3: Data Minimisation. Personal data shall be adequate, relevant and limited to what is necessary in relation to the purposes for which they are processed. This means organizations must not store any personal data beyond what is strictly required.
- Principle 4: Accuracy. Personal data shall be accurate and, kept up to date. This means organizations must have processes in place for identifying and addressing out-of-date, incorrect and redundant personal data.
- Principle 5: Storage Limitation. Personal data shall be kept in a form that permits identification of data subjects for no longer than is necessary for the purposes for which the personal data is processed. This means organizations must, wherever possible, store personal data in a way that limits or prevents identification of the data subject.
- Principle 6: Integrity & Confidentiality. Personal data shall be processed in a manner that ensures appropriate security of the personal data, including protection against unauthorized or unlawful processing, and against accidental loss, destruction or damage. GreenPoint organizations must use appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of personal data is always maintained.
- Principle 7: Accountability. The Data Controller shall be responsible for and be able to demonstrate compliance. This means organizations must demonstrate that the six data protection principles (outlined above) are met for all personal data for which it is responsible.
Data Subject Rights
Rights to
- Information access.
- Objection to processing.
- Objection to automated decision-making and profiling.
- Restriction of processing.
- Data portability.
- Data rectification.
- Data erasure.

